

Ongoing effects of the global COVID 19 pandemic are driving the need for manufacturers to develop strategies to address “new normal” operating conditions. At the same time, manufacturers continue to pursue digital transformation strategies targeted to deliver core business value in areas, such as improved business efficiency, competitive excellence, and market differentiation. 5G and private wireless both promise significant incremental performance improvements that meet the needs of these core business drivers and their associated connectivity requirements, as well as the shift toward increasingly automated and autonomous operations.
Ongoing improvements in cellular technology, including 4G LTE, 5G, and private wireless networks, are escalating the technology’s disruptive effect relative to alternatives, including WiFi. These improvements drive increased consideration of cellular technology as a primary communication medium vs. its historical use for network backup/failover and offline remote access and monitoring.
5G ultimately holds the promise of freeing connectivity from the limitations of wired infrastructure, enabling disruptive new applications. 5G’s low latency, high data rates, and massive capacity will accelerate adoption of industrial IoT edge capabilities in areas, such as AI/ML, AR/VR, edge computing, and mobility to enable truly autonomous robotics, logistics, and other manufacturing operations.
Cellular technology is well-suited for use in a growing number of mobile, remote, and outdoor applications, both in industry as well as transportation, smart cities, and public safety. Cellular is also the technology of choice for enabling increasingly important applications in personnel tracking and safety. This empowers the remote expert and connected worker, reducing the need for field service personnel.
Many customers targeting use of 5G and private networks are unfamiliar with using cellular technology in operations as opposed to remote access or network failover. Private 5G networks will require dedicated infrastructure buildouts and expanded ecosystem participation, increasing the investment cost and extending the installation timeline. Increasing availability of alternative connectivity technologies, including CBRS in North America and WiFi 6 worldwide, offers the potential for mixed-use scenarios.
Recognizing its rising potential in their served and targeted applications, industrial network infrastructure suppliers are increasing investment in their cellular product lines. Regional and global telecom providers are likewise targeting industrial, smart city, and public safety applications for growth, resulting in a broader array of cellular-based solutions intended for use in these growth segments.
Industry interest in 5G and private wireless stems from their perceived potential to accelerate today’s digital transformation strategies and associated business objectives. While specific objectives vary by customer, industry, etc., digital transformation strategies are generally tasked with improving business performance in areas, such as reduced cost, increased revenue, and improved business and process efficiencies. These long-term pursuits are now married with emerging objectives in areas such as operational resilience in the face of new business realities, competitive excellence and differentiation, physical and cyber security, and pursuit of product and service innovation.
New business realities include response to “new normal” business conditions dictated by the COVID-19 pandemic. This has heightened the need to reduce on-site personnel while simultaneously enabling remote capabilities for monitoring, troubleshooting, and training, as well as personnel tracking and safety. Business is likewise faced with the need to prepare and respond to ongoing and escalating physical and cyber security threats from both internal and external actors.
Several different paths to digital transformation are available to enable business improvement. Reduced downtime and maximum asset availability are core pursuits embodied in the Industrial IoT, while production flexibility and reconfigurability down to a batch size of one are the core tenets pursued with Industry 4.0.
Both automated and, ultimately, autonomous operations aid in meeting current and emerging business requirements. Automation has long been used to maximize production capability, reduce cost, improve product quality, and other core industrial pursuits. Autonomous operations extend this potential, including in ways that enable responses to the realities of the “new normal” business environment. For example, by reducing on-site personnel by deploying autonomous production robotics and logistics operations.
Business improvement strategies enabled by digital transformation require extensive data connectivity throughout the enterprise to feed both cloud and, increasingly, edge applications, such as analytics and machine learning. 5G and private wireless both promise significant connectivity performance improvements that meet the needs of Industrial IoT, Industry 4.0, and edge computing, as well as the shift toward increasingly automated and autonomous operations.
Many industrial customers have an historical view of cellular technology as a tool for remote access, network failover, outdoor installation, and/or for accessing locations that lack conventional network infrastructure. Ongoing technology improvements, starting with 4G LTE and now focused on 5G and private wireless, lead to increased consideration of cellular as a primary communications medium, including for indoor applications. Availability of private networks furthers the value proposition by eliminating reliance on public telecom networks and, depending on the approach, even the telecom operators themselves.
At its core, 5G technology holds the potential to fulfill the holy grail of industrial connectivity: freedom from the high cost and functional limitations of wired infrastructure. 5G’s low latency, high bandwidth, massive density and capacity, coupled with related developments such as TSN, make it technically capable of displacing today’s wireline, particularly Ethernet-based, approach to industrial connectivity.
Ultra-low latency and massive bandwidth will allow autonomous mobile robots and their support AGVs to communicate in real time while working on moving parts on a production line. Many industrial customers are also intrigued by concepts such as network slicing, which promises the potential to replace today’s multi-tiered architecture of dedicated enterprise, operations, and control networks with a single software-managed network infrastructure. This is due to the potential for lower operational costs and improved efficiencies.
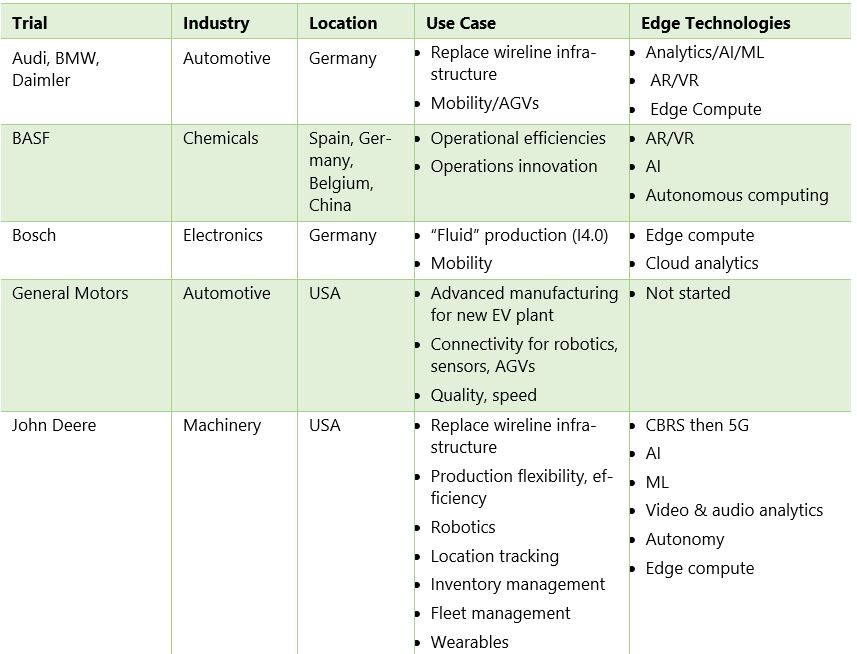
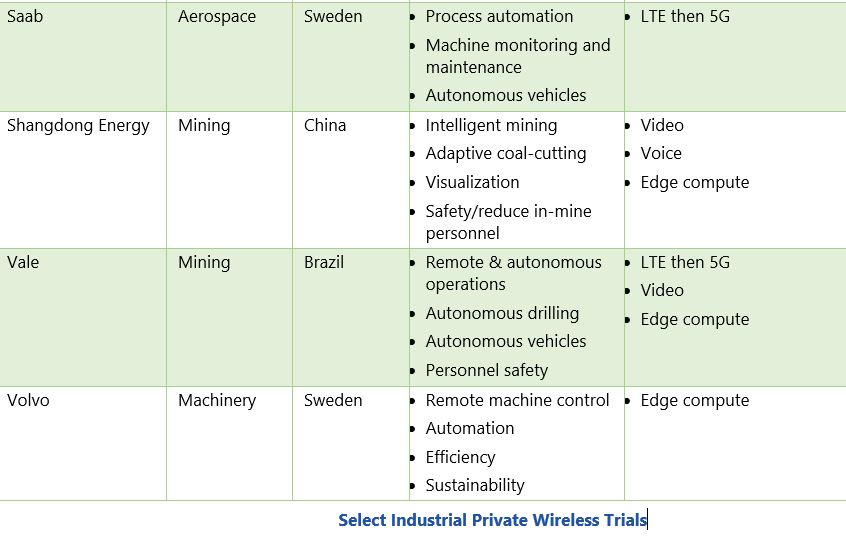
The use cases pursued in numerous industry trials of both 5G and private wireless indicate the perceived potential for incremental business improvements. These trials consistently reveal evaluation of AI/ML, AR/VR, edge computing, mobility, autonomous operations and logistics, and potentially disruptive new applications. The scope of current activity varies widely, from numerous off-line lab experiments and trial installations to GM’s stated intent to deploy the technology throughout their Factory Zero electric vehicle manufacturing facility, or Bosch’s vision to outfit 280 factories and generate €1 billion in annual revenue by 2022 from 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 solutions.
Manufacturers increasingly recognize that connected products, processes, and services can help generate not only business process improvement and potentially differentiated and innovative product and service offerings, but also further enable them to respond to the new normal business landscape. This is true in ways ranging from enabling remote asset access and monitoring to reducing field service and personnel training requirements through empowerment of, and access to, remote experts.
Availability of digitally transformed architectures is likewise leading some customers to further centralize or at least regionalize their operations. In this scenario, centrally located operations personnel leverage ubiquitous connectivity, edge and/or cloud-based applications, and universal visualization to monitor, access, and control large portions of geographically dispersed operations.
The low latency and massive capacity of 5G networks is also leading some customers to consider reversing the trend toward driving intelligence much further down into the architecture. Early 5G trials reveal that its higher bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and massive device density offers the potential to reverse the trend toward distributed intelligence. The enhanced connectivity enables computationally intensive analytics to be performed in a centralized device rather than distributing computing in lower-tier end devices. This ultimately reduces endpoint cost and complexity.
ARC Advisory Group clients can view the complete report at ARC Client Portal
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us

