

India pharmaceutical adopting automation technologies despite its pharmaceutical sector having been traditionally based largely on manual operations. It is now adopting new automated operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) to remain competitive in a connected world. Only through continuous innovation and judicious adoption of new technologies will companies in this sector, domestic and global, succeed in surmounting today’s challenges. These include:
Considering India’s continuing strength in the IT services space, pharmaceutical companies should leverage this local expertise to modernize operations and implement new Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)-related technologies and approaches such as smart 
ARC Advisory Group believes that pharmaceutical enterprises will need to rapidly embrace mobility, cloud, and other automation and IT technologies and standards because the risk of not deploying them could be greater than the risk typically associated with deploying new technology…even if this should require costly and time-consuming revalidation of equipment and processes.
This Insight highlights some technology trends that are shaping the new business environment with specific reference to India’s pharmaceutical sector. Clearly, technology implemented at the micro level will impact the macro level. When deploying new technology brings quantifiable benefits for one domestic company, other domestic companies will also adopt it; then companies in other countries adopt it and the global reach expands.
The pharma sector in India needs to take a closer look at both new operational technologies (such as wireless sensors and automation) and new information technology (ERP, EAM, MES, SCM, IoT, etc.)
Increased automation can help the pharmaceutical industry make more efficient usage of energy and raw materials; improve safety in working conditions; enhance regulatory compliance, and improve both product quality and consistency. Information technology brings in the much–needed interconnectivity between equipment, operations, and people.
India’s IT and pharmaceutical sectors are closely linked. While lower cost competitors are emerging in this space, India remains a favored destination for IT outsourcing; while India’s pharmaceutical industry is the world’s third largest in terms of volume. Today, India’s pharmaceutical industry is implementing technology for process management, data analytics, content management, identifying cost-effective therapies, and to engage with the healthcare providers and customers.
Connected devices in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities help improve business and manufacturing efficiency and reduce risk by enabling:
IT and operational technologies (OT) in the pharmaceutical industry decreases the manual work, enables e-documentation, improves competitiveness, and reduces time-to-market. Automated IT systems or IT-supported automated processes for this sector include: enterprise resource planning (ERP); electronic batch record systems (EBRS); manufacturing execution systems (MES); quality management systems (QMS); and mobile technology, to name a few.
In a digital world, pharmaceutical companies must deploy these types of next-generation technologies to streamline and improve their manufacturing and business processes. They need to strive for real-time transparency of their R&D; smooth sales and operations planning in the supply chain; as well as meet new standards and expectations in efficiency and agility. The IT-OT (operations technology) convergence is now becoming a reality.
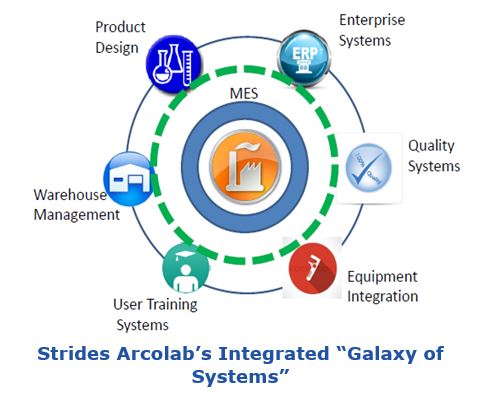
Strides Arcolab took an integrated approach using a “galaxy of systems” with the core focus on manufacturing surrounded by a layer of manufacturing execution systems (MES). These include laboratory information management systems (LIMS), quality management systems (QMS), building automation and control systems (BMS), and warehouse management systems (WMS). According to the presenter, this IT-OT convergence approach resulted in world class manufacturing and a total business transformation.
Technology can play a pivotal role in driving success in India’s pharmaceutical industry and some companies are already on the right path. However, as technology advances, there are associated risks and challenges when it comes to security and data privacy in the pharmaceutical industry. The security angle must be addressed by all pharmaceutical companies via investment in IT and developing a culture of prevention. And, of course, the potential benefits of implementing new technology must be balanced against the cost, time, and effort required to validate new equipment, systems, and/or processes to meet US FDA and other governmental requirements.
The lines between IT and OT are blurring as the “3Cs” - connectivity, communication, and collaboration are now recognized as business enablers.
Based on ARC research and analysis, we recommend the following actions for owner-operators and technology providers:
For Owner-Operators:
For Technology Providers:
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us
Keywords: India, Pharmaceutical Industry, Automation, Technologies, IIoT, IT, Regulatory Compliance, Case Study, ARC Advisory Group.

